Developing Applications for iOS using SwiftUI
Total Lecture: 15
current: [7-9]
Shape,ViewModifier,Constants
Constants
1 | struct CardView: View { |
Shape
Shape是一个继承自View的协议,RoundedRectangle,Circle,Capsule
默认情况下,Shapes用当前foreground color来填充,可以通过.stroke()和.fill()来改变,stroke()、fill()是形状修饰符,而不是视图修饰符。它们本质上是一些小函数,利用shape并对其进行描边或填充来创建视图
1 | func fill<S>(_ whatToFillWith: S) -> View where S: ShapeStyle |
ShapeStyle就是知道如何获取Shape,并对其进行处理以将其转换为View的东西,比如Color,ImagePaint,AngularGardient,LinearGradient
Custom Shape
1 | func path(in rect: CGRect) -> Path { |
Animation
制作动画的一种方法是对Shape进行动画处理。另一种是通过ViewModifiers
动画只是变化的可视化
ViewModifier
.aspectRatio(2/3)等同于.modifier(AspectModifier(2/3))AspectModifier可以是遵从ViewModifier协议的其他东西,这里只是语法糖
ViewModifier Protocol
1 | protocol ViewModifier { |
调用方式
1 | aView.modifier(MyViewModifier(arguments:...)) |
Cardify ViewModifier demo
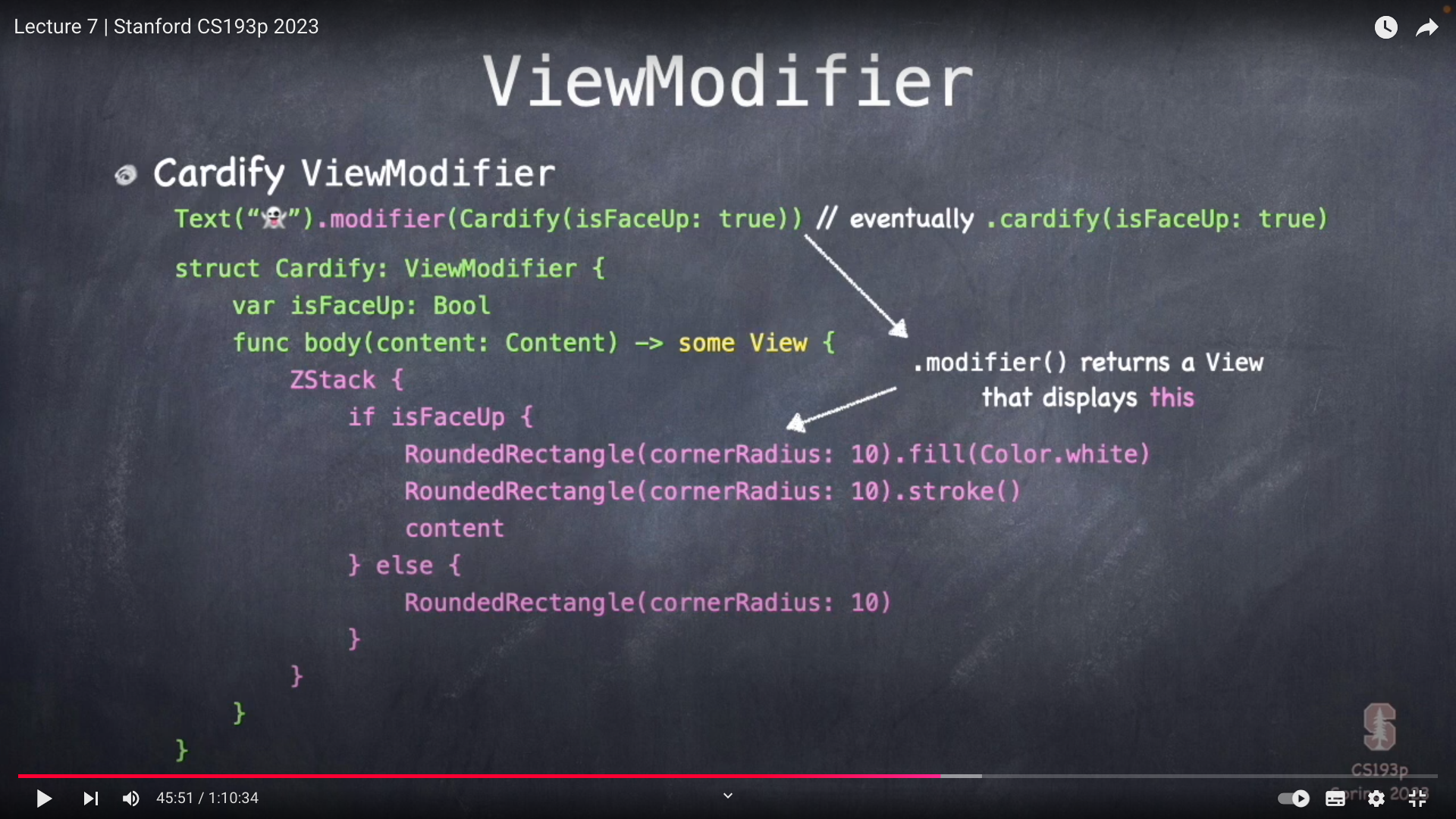
ViewModifier 语法糖
Text("🐶").modifier(Cardify(isFaceUp: true)) 等同于 Text("🐶").cardify(isFaceUp: true)
1 | extension View { |
Protocol (part 2)
协议最大用途是代码共享(code sharing),可以通过extension添加默认实现方法,协议只是事物的声明,而不是实现
filter
可作用于 Array, Range,String,Dictionary
1 | filter(_ isIncluded: (Element) -> Bool) -> Array<Element> |
它是Sequence协议的extension
View
1 | protocol View { |
默认实现
1 | extension View { |
Generics + Protocols (通用协议)
1 | protocol Identifiable { |
类型ID是 don’t care for Identifiable,不过必须遵从Hashable协议
1 | protocol Identifiable { |
或者简写
1 | protocol Identifiable { |
some
可用于协议的不透明(opaquely)类型 传入传出于 func/var
不透明意思是,只知道它的协议类型,不知道具体类型
1 | func getShape(rounded: Bool) -> some Shape { |
any
any本质上是一种拥有一个异构数组或容器,里面装满了响应协议的东西的方法
let ids = [any Identifiable]()
1 | func printId(of identifiable: some Identifiable) { |
Animation(Pard 1)
Property Observers and .onChange(of:)
Swift可以检测所有这些值类型何时发生变化,函数被标记为mutaing,所以我们知道哪些函数会修改事物。对于变量,它知道哪些变量是settable,gettable
1 | var isFaceUp: bool { |
属性观察不能用于@State,@Published变量,在视图中需使用.onChange(of:){},它是一个modifier
1 | private var taps = 0 |
Animation
动画只是展示模型随时间发生的变化,通过ViewModifier参数反映出来,显然Shape也可以改变。
ViewModifer是UI中的主要变更代理
Implicait Animation
1 | .animation(Animation, value:) |
根据某些动画曲线,对这些的更改就会得到动画。
1 | Text("🐶").opacity(card.scary ? 1 :0 ) |
.animation 通常用于”Lego brick”视图(叶子视图),或与所有其他视图完全独立的视图,而不是容器视图上
什么时候使用隐式动画?
无论发生什么,你都希望这件事发生,它完全独立于任何其他”withAnimation”,或正在发生的任何其他事情,而且它也会覆盖它,比如显示执行的动画
如何关闭动画?
1 | private var score: some View { |
Explicitly
使用withAnimation来包装我们正在做的事情,它使得我们在里面发生改变的所有事物一起动画起来,这也是实现动画的主要方式。
1 | withAnimation(Animation) { } |
常用于用户交互动画
Animation Curve
动画曲线是如何分割动画所需的时间
1 | .linear |
Transitions
only work on Views that are inside Containers That Are Already On-Screen.
只在当前显示的容器下有效
所有transition API都是擦除类型(type erased)
1 | ZStack { |
将transition视为名词,这是当该视图出现或消失时使用的过渡,实现过渡动画的方式,是将视图移出或放在屏幕上,这是动画发生的原因。
Matched Geometry Effect
有时你想将一个视图从一个地方移动到另一个地方
两个视图不在同一个容器内时
1 | .matchedGeometryEffect(id: ID, in: Namespace) // ID type is a "don't care": Hashable |
.onAppear
如何在视图显示在屏幕上时立即启动动画?
.onAppear{}
Shape and ViewModifier Animation
所有动画发生在Shapes和ViewModifiers,Transitions和matchedGeometryEffect是匹配(paired)的ViewModifiers
the animation system divides the animation’s duration up into little pieces, the Shape/ViewModifier makes sure its body draws appropriately at any “piece” value
ViewModifier要做的就是监听动画系统,绘制它应该绘制的部分,然后动画系统会处理剩下的事情。动画系统如何与你的ViewModifier对话,并告诉它要绘制什么部分等等?它通过一个名为animatableData变量来实现
animatableData
communication with the animation system with a single var, int the Animatable protocol
任何想要实现动画的ViewModifier或Shape都需要实现Animatable协议
1 | var animatableData: Type |
Type是don‘t care类型,需实现VectorArithmetic协议
AnimatblePair实现了VectorArithmetic ,包含两个VectorArithmetics
animatableData是read-write var
setting是动画系统告诉Shape/VM which “piece” to draw
getting是动画系统获取动画的开始结束点 start/end points
Animation(Pard 2)
TimelineView
TimelineView是一个非常简单的视图,需要你提供的任何ViewBuilder,然后执行动画操作,将其切成小块(pieces)并反复调用
1 | struct CardView: View { |
1/5 秒刷新一次
当你从视图层次结构中移除或添加视图时,不透明度是使用的默认转换
1 | .transition(.scale) |
发牌动画如何实现?
让这些卡片在其容器出现在屏幕上之后出现
1 | private var cards: some View { |
在视图中实际没有@State,唯一的@State是临时状态,面向UI的状态,发牌是一个UI的事情,它不是游戏的一部分,存粹是UI的一部分,这是@State的一个很棒、明显的用途。
MatchedGeometryEffect
1 | private var dealingNameSpacing |